In recent years, the summer temperature has been rising, but to understand why, we need to study the mechanism of atmospheric circulation. The global environment is made up of many mechanisms, such as the circulation of the atmosphere, water, and soil. Here, we will unravel the mechanism of atmospheric circulation. There are two main circulations of the atmosphere: land and sea. In both, plants are found to be an important circulatory element.
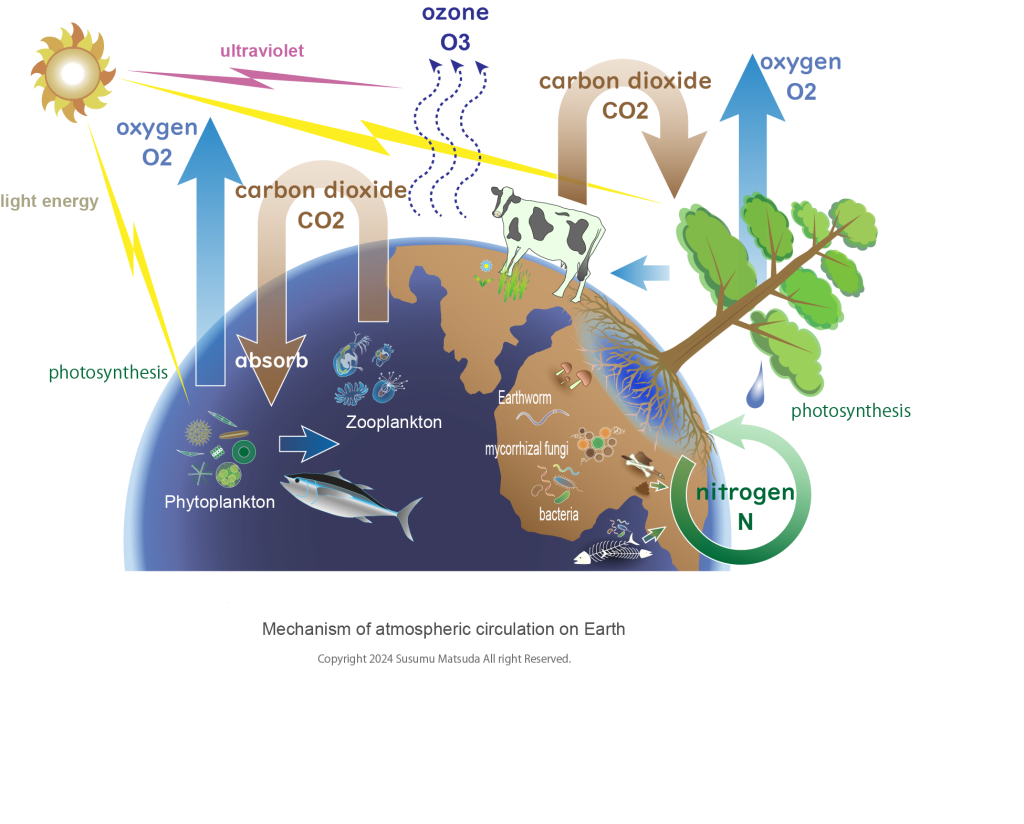
On land, trees live as plants and play a central role in the circulation of the atmosphere. Plants absorb nitrogen, nitrates, inorganic salts, etc. that they can absorb from the ground, absorb carbon dioxide from their leaves, and produce oxygen and sugar through photosynthesis. Animals eat plants, absorb oxygen, and release carbon dioxide. Animal carcasses and the feces they excrete produce nitrogen. In addition, organisms and fungi that live in the soil become corpses and produce nitrogen when they finish their activities. Molds and fungi that live in the soil process corpses in the soil and produce nitrogen. Phytoplankton that live in the sea absorb carbon dioxide and produce oxygen through photosynthesis. Zooplankton absorb phytoplankton, which are then preyed upon by fish in the ocean. Living creatures such as fish take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide. Fish waste releases nitrogen. Fish also release nitrogen when they die and finish their activities. Nitrogen produced by recent deposits in the ocean dissolves into the water as nutrient salts. The water cycle and atmospheric cycle introduced in blog 209 act as a mechanism for circulating between the ocean and land. The Earth’s ecosystem is made possible by various cycles, and the environment continues to thrive. Maintaining ecosystems has an effect on the global environment and ensures people’s peace of mind.